Abstract
Objectives
High failure rates of metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty implants have highlighted the need for more careful introduction and monitoring of new implants and for the evaluation of the safety of medical devices. The National Joint Registry and other regulatory services are unable to detect failing implants at an early enough stage. We aimed to identify validated surrogate markers of long-term outcome in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Methods
We conducted a systematic review of studies evaluating surrogate markers for predicting long-term outcome in primary THA. Long-term outcome was defined as revision rate of an implant at ten years according to National Institute of Health and Care Excellence guidelines. We conducted a search of Medline and Embase (OVID) databases. Separate search strategies were devised for the Cochrane database and Google Scholar. Each search was performed to include articles from the date of their inception to June 8, 2015.
Results
Our search strategy identified 1082 studies of which 115 studies were included for full article review. Following review, 17 articles were found that investigated surrogate markers of long-term outcome. These included one systematic review, one randomised control trial (RCT), one case control study and 13 case series. Validated surrogate markers included Radiostereometric Analysis (RSA) and Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse (EBRA), each measuring implant migration and wear. We identified five RSA studies (one systematic review and four case series) and four EBRA studies (one RCT and three case series). Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) at six months have been investigated but have not been validated against long-term outcomes.
Conclusions
This systematic review identified two validated surrogate markers of long-term primary THA outcome: RSA and EBRA, each measuring implant migration and wear. We recommend the consideration of RSA in the pre-market testing of new implants. EBRA can be used to investigate acetabular wear but not femoral migration. Further studies are needed to validate the use of PROMs for post-market surveillance.
Cite this article: T. T. Malak, J. A. J. Broomfield, A. J. R. Palmer, S. Hopewell, A. Carr, C. Brown, D. Prieto-Alhambra, S. Glyn-Jones. Surrogate markers of long-term outcome in primary total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Bone Joint Res 2016;5:206–214. DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.56.2000568.
Article focus
-
Systematic review.
-
Current surrogate markers of long-term revision rate in primary Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA).
Key messages
-
Radiostereometric Analysis (RSA) is validated to predict long-term revision rates within two years post-operation in relation to acetabular wear and femoral migration.
-
Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse (EBRA) is validated to detect acetabular wear to predict long-term revision rates but not femoral migration.
-
Further research is needed to investigate other potential surrogate markers such as Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) for post-market surveillance.
Strengths and limitations
-
Strict inclusion criteria were adopted that may have led to the exclusion of potential surrogate markers.
-
RSA and EBRA only detect migration and wear which predicts failure due to aseptic loosening, and not other modes of failure.
Introduction
The recent high failures of metal-on-metal (MoM) implants for primary total hip arthroplasty (THA) have highlighted the need for the early identification of failing implants.1 However, European regulation falls short of providing safety monitoring. Manufacturers require a Conformité Européenne (CE) mark to allow for their implants to be marketed and used in patients. This CE mark can be obtained from any one of 76 bodies in Europe2,3 with approval required from only one governing body to permit marketing of the device. Despite orthopaedic devices classified as ‘Class III’ requiring clinical evidence for their use, manufacturers can still introduce a Class III product without new evidence in the event that evidence for a similar existing device is demonstrated.3 However, in the United Kingdom, the Medical Devices Regulation and Safety (MHRA) requires the submission of clinical follow-up for all new products once CE approval is given. A recent systematic review has shown that 24% of all hip implants used in the United Kingdom in 2011 had no evidence to support their clinical effectiveness.4 However, this study did not explore the clinical evidence submitted by manufacturers for marketing approval.
In response to concerns with device regulation, a new framework for the phased introduction of new implants was developed by the ‘IDEAL’ Collaboration. This involves a five-stage process: Idea, Development, Exploration, Assessment, Long-term follow-up.5,6 IDEAL calls for the continual monitoring of newly introduced implants to ensure their safety. In addition, the British Orthopaedic Association and Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency initiated the “Beyond Compliance” project,7 which further highlights the need for the safe introduction of new implants with high-quality monitoring. However, both of these schemes are voluntary and rely on the collection of basic post-market surveillance data along with revision rates.
The monitoring schemes currently in place include the National Joint Registry (NJR)8 and the Orthopaedic Data Evaluation Panel (ODEP).9 The NJR is primarily designed to assess long-term outcome by monitoring revision rates, however, it is of limited use in screening new implants as it cannot identity outliers during the first few years of implant use.10 The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) states the benchmark for a hip arthroplasty implant is a revision rate of less than 5% at ten years post operation.11 However, revision is a rare occurrence and implants are initially used in small numbers; the use of revision rate as an early indicator of late failure has been unsuccessful.1 This point is best highlighted by the introduction of MoM implants, particularly the Articular Surface Replacement (ASR, DePuy, Raynham, Massachusetts). Nearly 100 000 ASR devices were implanted worldwide, 10 000 in the United Kingdom alone, before problems were identified with the delay resulting in significant harm to many patients.1,12 ODEP is a voluntary scheme under the NHS to capture data on new implants at three-, five- and ten-year intervals. At each interval, a rating is given with ‘A*’ now being the highest based on performance and strength of supporting evidence.9 There are three grades for each follow up interval. Grade A* requires revision rates of less than 5% at ten years within a cohort of 500 patients at the start of the study from more than three centres. Grade A requires better than or equal to 90% survival rate with the same criteria for the cohort. Finally, grade B requires a minimum of 100 patients with a survival rate of better than or equal to 90%.9 However, the performance is dependent on revision rate and therefore may not be able to identify failing implants early. Notably, the ASR implant had the highest ODEP rating at the time (‘3A’) before any problems were identified.13
The current system for implant monitoring is therefore inadequate, as it cannot identify poorly performing implants until many thousands have been inserted. In response, both the IDEAL group and Beyond Compliance have suggested a phased introduction of new implants through pre-market clinical testing prior to the national introduction of a new implant.6,7,14,15 However, this process can only be delivered with the aid of a cost-effective, simple surrogate outcome measure that can yield clinically useful predictions of future function within two years of an implant being introduced.
Materials and Methods
Objective
We performed a systematic review to determine whether there are validated surrogate markers of long-term revision for primary THA implants.
Eligibility criteria
A systematic review of the literature was conducted according to Cochrane guidelines.16,17 Eligible studies included any systematic review, randomised control trial, cohort, or case-control study investigating a surrogate marker in predicting long-term outcome in primary THA in vivo.
NICE considers a proven implant to have a revision rate of < 5% at ten years.11 Therefore, long-term outcome was defined as revision rate of an implant at ten years. However, we also included studies that compared a surrogate marker with revision rate from seven to ten years. We investigated for all modes of failure excluding fracture, dislocation and infection.
Surrogate markers are defined as a measure that can reasonably predict a clinical outcome of interest, regardless of whether it directly measures that clinical outcome.18 A surrogate marker differs from a risk factor or predictor; a risk factor is present before surgery and affects the outcome (revision) whilst a surrogate marker is present after the operation and correlates with the outcome. We are specifically investigating markers that have been shown to correlate with long-term revision rate.
We included studies that used inferential statistics to investigate the measure of a surrogate marker compared with late revision rate (e.g. regression, chi-squared, sensitivity/specificity, ROC curve univariable/multivariable analysis).
Studies involving hip fracture/dislocation/infection, revision THA, animals and in vitro investigations, or predicting an outcome other than revision were excluded.
Validated surrogate markers were classified as any method measured within the first two post-operative years that was statistically shown to correlate with overall implant revision rate at ten years.
Search strategy
We did not publish a protocol and this systematic review was not pre-registered. A broad search strategy was developed for Medline and Embase (OVID) databases. Separate search strategies were devised for the Cochrane database and Google Scholar.
The search strategy terms for Medline, Embase and Cochrane databases can be found in Table I. We used the following terms to search Google Scholar database: Prediction / long-term / ten-year / outcomes / hip arthroplasty / hip replacement.
Table I.
Medline, Embase and Cochrane search strategies
| MEDLINE | EMBASE | COCHRANE |
|---|---|---|
| 1. exp ARTHROPLASTY, REPLACEMENT, HIP/; 17320 results. | 20. exp TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY/ OR exp TOTAL HIP PROSTHESIS/ OR exp TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT/; 22279 results. | 1 MeSH descriptor: [Arthroplasty, Replacement, Hip] explode all trees 1616 |
| 2. (hip* ADJ3 replacement*).ti,ab; 11179 results. | 21. hip* ADJ3 arthroplast*).ti,ab; 18277 results. | 2. outcomes:ti,ab,kw (Word variations have been searched) 201113 |
| 3. (total ADJ3 hip ADJ3 replacement).ti,ab; 7138 results. | 22. 20 OR 21; 30071 results. | 3 MeSH descriptor: [Treatment Outcome] 1 tree(s) exploded 95982 |
| 4. (total ADJ3 hip* ADJ3 arthroplast*).ti,ab; 12131 results. | 23. exp TREATMENT OUTCOME/ OR exp OUTCOMES RESEARCH/; 1017012 results. | 4 joint revision 651 |
| 5. (hip* ADJ3 arthroplast*).ti,ab; 16151 results. | 24. outcome*.ti,ab; 1309132 results. | 5 revision rate 1722 |
| 6. 1 OR 2 OR 3 OR 4 OR 5; 29953 results. | 25. “patient outcome*”.ti,ab; 36798 results. | 6 MeSH descriptor: [Prosthesis Failure] this term only 589 |
| 7. exp TREATMENT OUTCOME/ OR exp TREATMENT FAILURE/; 673333 results. | 26. exp PROGNOSIS/; 469482 results. | 7 prognosis 18172 |
| 8. outcome*.ti,ab; 964585 results. | 27. exp PROSTHESIS FAILURE/; 27986 results. | 8 MeSH descriptor: [Reoperation] this term only 1647 |
| 9. exp PROGNOSIS/; 1122139 results. | 28. exp REOPERATION/; 52851 results. | 9 MeSH descriptor: [Patient Outcome Assessment] this term only 13 |
| 10. exp PROSTHESIS FAILURE/; 21934 results. | 29. (joint* ADJ3 revision).ti,ab; 362 results. | 10 #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 214295 |
| 11. exp REOPERATION/; 67049 results. | 30. (revision ADJ3 rate*).ti,ab; 2631 results. | 11 MeSH descriptor: [Forecasting] this term only 505 |
| 12. (joint* ADJ3 revision).ti,ab; 319 results. | 31. 23 OR 24 OR 25 OR 26 OR 27 OR 28 OR 29 OR 30; 2297641 results. | 12 prediction 5437 |
| 13. (revision ADJ3 rate*).ti,ab; 2220 results. | 32. exp PREDICTION/; 230887 results. | 13 predictor 7330 |
| 14. 7 OR 8 OR 9 OR 10 OR 11 OR 12 OR 13; 1828944 results. | 33. prediction*.ti,ab; 228449 results. | 14 predict* ADJ3 outcome* 833 |
| 15. prediction*.ti,ab; 196780 results. | 34. predictor*.ti,ab; 311190 results. | 15 #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 13100 |
| 16. predictor*.ti,ab; 223411 results. | 35. (predict* ADJ3 outcome*).ti,ab; 72916 results. | 16 #1 and #10 and #15 3 |
| 17. (predict* ADJ3 outcome*).ti,ab; 50942 results. | 36. 32 OR 33 OR 34 OR 35; 647538 results. | |
| 18. 15 OR 16 OR 17; 425222 results. | 37. 22 AND 31 AND 36; 578 results. | |
| 19. 6 AND 14 AND 18; 467 results. |
Each search was performed to include articles from each database from the date of their inception to June 8, 2015. No restriction of language was applied, however, if we were unable to obtain a translation of an article, it was excluded. We did not exclude any articles.
Two reviewers (TTM, JAJB) independently performed the initial screening of articles identified from our search strategy based on the title and abstract. Full articles for review were obtained and re-examined according to our inclusion criteria. Finally, the references of any relevant articles were also screened. A third author (AJRP) resolved any discrepancies.
Statistical analysis
A standardised data extraction form was used to obtain information concerning each eligible study identified. Information extracted included: year of publication, design, level of evidence, sample size, type of surrogate marker, and primary outcome, including statistical significance where relevant. The two reviewers extracted data from relevant articles independently and compared forms separately in order to minimise errors.
We were unable to perform a meta-analysis due to the limited number and heterogeneous nature of the included studies. Risk of bias was not performed as the majority of studies were not trials. For the two systematic reviews included, risk of bias was performed within their respective studies.
We have identified themes of validated surrogate markers of long-term outcome in primary THA and report these findings descriptively. We accepted a statistical value of significance to be p ⩽ 0·05 when determining the validity of a surrogate marker.
Results
Search strategy outcome
Following a search of Medline, Embase, and Cochrane databases, 1048 studies were identified. A search of Google Scholar and references of included articles identified a further 35 studies totalling 1083 possible studies. We performed a key word search of the ClinicalTrials.gov and NHS Evidence databases, which identified no further relevant trials or studies. Following exclusion as per the criteria outlined above, 116 studies were obtained for full article assessment. Details of the screening and exclusion are provided in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Fig. 1).
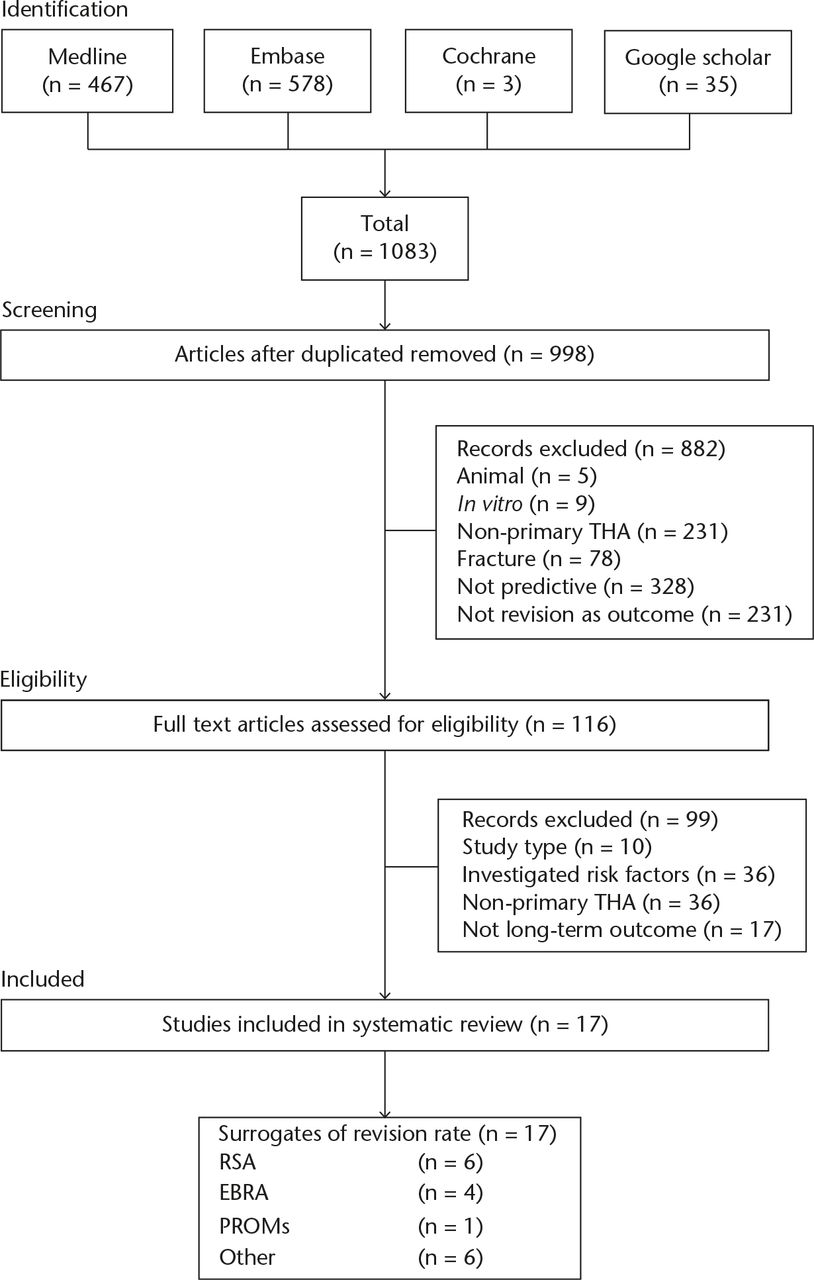
Fig. 1
Study Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flowchart THA, total hip arthroplasty; RSA, radiostereometric analysis; EBRA, Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse; PROMs, patient-reported outcome measures
A total of 17 studies met the inclusion criteria for our systematic review and assessed the use of surrogate markers of long-term outcome in primary THA (Table II). This included two systematic reviews, one randomised control trial (RCT), one case control and 13 case series.
Table II.
Characteristics of included studies investigating a surrogate marker of outcome in primary total hip arthroplasty
| Reference | Design | Sample Size | Surrogate Marker | Implant Type | Follow-up | Primary Outcome | Correlation with Revision | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sesselmann S et al 201319 | Systematic Review | 309 | RSA | All | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | None |
| Pijls B G20 | Systematic Review | 700 | RSA | Acetabular components | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Migration of 1.0 mm was considered unacceptable |
| Hauptfleisch J et al 200621 | Case Series | 118 | RSA | Cemented | 9 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Significant difference in posterior head migration p = 0.002 |
| Nieuwenhuijse M et al 201222 | Case Series | 39 | RSA | Cemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Continued subsidence associated with higher revision p < 0.001 |
| Karrholm J et al 199423 | Case Series | 84 | RSA | Cemented | 7 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Subsidence > 1.2 mm at two years associated with higher revision p < 0.000005 |
| Freeman M et al 199424 | Case Series | 206 | RSA | Cemented | 7 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Subsidence > 1.2 mm at two years associated with higher revision p < 0.003 |
| Krismer et al 199925 | Case Series | 240 | EBRA - Femoral | Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | N | Subsidence > 1.0 mm at two years associated with higher revision p = 0.0001 |
| Krismer et al 199626 | RCT | 120 | EBRA - Acetabular | Uncemented | 8 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Subsidence > 1.5 mm at two years associated with higher revision p = 0.005 |
| Mazoochian F et al 200727 | Case Series | 10 | EBRA | Uncemented | 7 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | N | None (Descriptive) |
| Hendrich C et al 200628 | Case Series | 11 | EBRA | Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year Migration | Y | Subsidence > 1.0 mm at two years associated with higher revision p = 0.002 |
| Takenaga R et al 201229 | Case Series | 50 | PROMs Functional Tests | Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs 21 Day Test | N | No association p > 0.05 |
| Kobayashi A et al 199730 | Case Series | 575 | X-ray Migration | Plain Radiograph Assessment | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 Year Assessment | Y | Subsidence > 2.0 mm at two years associated with higher revision p < 0.0001 |
| Ranawat C et al 199531 | Case Series | 236 | X-ray Bone-Cement Interface | Plain Radiograph Assessment | 10 | Revision Rate vs Bone-Cement Interface | Y | Observer rated radiographs deemed as loose at 1 year associated with higher revision rate p = 0.002 |
| Dowd J et al 199432 | Case Series | 48 | Digitizer Programme - Migration | Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs Digitizer Programme | Y | Subsidence > 0.3 mm per year p < 0.001 |
| Malik M et al 200533 | Case Control | 201 | Post Op X-ray (Wear in Gruen Zones) | Cemented Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs Post Op X-ray | Y | Thickness of cement mantle in Gruen zones 6 and 7 associated with higher revision rate p = 0.040 and p = 0.003 Radiolucent lines in zone 3 and 5 p = 0.0001 |
| Scott G et al 200634 | Case Series | 143 | X-ray Migration using Digitizer | Cemented Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs X-ray Migration at 3 years | Y | Subsidence > 3.0 mm at three years associated with higher revision p < 0.0001 |
| Khalily C et al 199835 | Case Series | 119 | X-ray Assessment (Wear in Gruen Zones) | Uncemented | 10 | Revision Rate vs 2 year X-ray Assessment | Y | Wear in Gruen zones 1,7,8 and 14 at 2 years associated with higher revision rate p < 0.001 |
-
RSA, radiostereometric analysis; EBRA, Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse; PROMs, patient-reported outcome measures
The surrogate markers identified are implant migration and wear, and patient reported outcome measures (Table III).
Table III.
Surrogate markers of long-term outcome in primary total hip arthroplasty
| Surrogate marker | n | Predicts revision rate | Does not predict revision rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiostereometric Analysis –Migration and Wear | 6 | 619-21,23,24,36 | – |
| Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse – Migration and Wear | 4 | 226,28 | 225,27 |
| Functional Outcome Score | 1 | – | 129 |
| Wear on standard radiographs | 6 | 630-35 | - |
| Total | 17 | 14 | 3 |
Implant migration and wear
Ten of the 17 studies validated the use of implant migration and wear (both acetabular and femoral components) within the first two years post-operatively as a surrogate marker for failure (Tables II and III). Two techniques most commonly used included the Radiostereometric Analysis (RSA) and Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse (EBRA).
A total of six studies used RSA to predict long-term revision rate (two systematic reviews19,20 and four cases series21-24). Stem migration of more than 1 mm to 2 mm in two years correlated with an increased rate of revision in two studies.19,21 Uncemented stems are designed to have minimal or no migration after two years, further migration is associated with an increased risk of higher revision rates.19 However, cemented stems can undergo ongoing migration after two years, but less than 2 mm in two years correlates with a late revision rate. The important migration for uncemented stems is distal migration, whereas for cemented stems is femoral head posterior migration.
Acetabular proximal migration ranged from 0.17 mm to 0.24 mm in the first year. A significant wear rate was calculated as more than 0.1 mm per year in all studies investigating acetabular wear. One study found the mean accuracy for RSA in clinical studies to be between 0.1 mm and 0.2 mm for translation, with a range from 0.05 mm to 0.5 mm, and rotational accuracy is between 0.15° to 1.15°.19
Four studies used Einzel-Bild-Röntgen-Analyse (EBRA) to measure migration of either the acetabular or femoral component (one RCT26 and three case series25,27,28). The quoted accuracy of EBRA is 1.0 to 1.5 mm for the femoral component and 0.8 mm to 1 mm for the acetabular component in all included studies. One study showed EBRA as having a mean difference of 0.08 mm for the measurement of acetabular wear when compared with RSA.
Other types of surrogate outcome markers
A total of six studies compared other types of surrogate outcome markers (one case control33 and five case series30-32,34,35). These included analysis of wear in standard radiographs. Although these methods showed potential as surrogate markers, they have largely been superseded by the accuracy and precision of RSA and EBRA.
Functional outcome score
One of the 17 studies investigated the association between functional scores against long-term revision rates (one case series).29 No significant relation between the 6-minute walk, Harris Hip (HH), SF-36, and Tegner Lysholm scores and subsequent revision rate at ten years was shown.37
Discussion
In this study, we systematically reviewed the literature for studies investigating surrogate markers for predicting long-term outcome in THA. The main validated methods include migration and wear measurements through RSA and acetabular wear measurements via EBRA. We found EBRA to be accurate in measuring wear and acetabular migration, but the accuracy in measuring femoral stem migration is poor. Therefore, its use as a surrogate marker of revision for THA may not be adequate to identify failing implants due to femoral wear. Alternatively, RSA has the accuracy and precision to measure stem and acetabular migration in addition to wear.
Surrogate imaging methods seem to show the most promise for identifying devices that are likely to fail prematurely by aseptic loosening but these methods need to have an accuracy of at least 0.1 mm to 0.2 mm38,39 in each dimension in order to detect bearing surface wear. RSA is a three-dimensional imaging technique which involves inserting metal beads into the femur and acetabulum to analyse the movement of an implant in relation to its host bone over two years.40 Several studies have validated the use of RSA against long-term revision rate. This method is very attractive as it is highly accurate and therefore requires small RCTs in order to draw meaningful conclusions about the longevity of an implant.19,41 RSA is able to measure migration for both cemented and uncemented femoral stems as well as the wear of hard-on-soft bearing surfaces.42 However, RSA is difficult to implement, requiring the use of specialist equipment and is thus only performed in a few centres worldwide. Moreover, some types of RSA require implants with attached marker beads to be specially manufactured and therefore the implant design may differ from that of the marketed implant.43,44 Although RSA has been shown to identify failing implants early, it may not be a universal method of monitoring new implants to detect all types of failures. In the case of the ASR implant, the mode of failure would not have been detected by implant migration.45
EBRA, in contrast to RSA, is a two-dimensional imaging programme that measures migration and wear. Individual programmes exist for measurement of wear and acetabular or femoral component micromovement.46 Evidence for EBRA was mixed with two studies showing correlation and two which did not.25-28 EBRA has adequate accuracy to measure acetabular component migration and wear (threshold 0.1 mm per year),47 but with a femoral component migration measurement accuracy of only 1 mm to 1.5 mm, EBRA may only be suitable for measuring bearing surface wear.19
A potential alternative to imaging is the use of PROMs and functional assessment at 21 days. Although we found no evidence that the HHS predicts revision rates, the Oxford Hip Score (OHS) does show promise;48 a poor OHS score (less than 27) at six months predicted higher early revision rates within two years.48 However, this was not validated against long-term revision rates. Using patient reported outcomes as a surrogate marker has potential benefits over RSA, as the cost of RSA is in the region of £250 000 per trial for each new implant tested, and furthermore, RSA is technically difficult to perform, as it requires specialist equipment and expertise. In the United Kingdom, PROMs are routinely collected for all patients undergoing THA, and is therefore simpler and potentially far less costly than RSA.49 In the future, it may be that PROMs will be a better target as a surrogate marker of long-term outcome due to its cost effectiveness. However, only OHS at six months has been shown to predict revision rates at two years.48 Moreover, existing PROMs may not be able to predict long-term implant failure, as implant loosening is a gradual process which only presents with symptoms in its final stages.50 In addition, the validation of PROMS as a surrogate measure is likely to require large study numbers to ensure sufficient power for statistical calculations, meaning new implants will need to be used in thousands of patients, with obvious additional costs. In contrast, RSA requires a minimum of 30 patients to predict long-term outcome, and thus is more appropriate for pre-market testing, while PROMs may be used in post-market surveillance to monitor implants after their general introduction.
Limitations
Our study used a search strategy with strict inclusion and exclusion criteria. In particular, we included only studies that investigated surrogate markers predicting long-term outcome. Studies investigating markers relating to early revision rates were not included. Therefore, we may have missed some potential surrogate markers. Any study investigating a surrogate marker against mid-term revision rates was analysed but yielded no further results for our systematic review. Furthermore, the search strategy included the term ‘predict’, thus papers focusing on a causal path or association to failure may have been missed. There is a lack of available indexing terms and so we accept that it would still be possible to miss potential studies. However, a surrogate marker is different to a predictor. Despite this, the term surrogate marker is defined as a measure that can reasonably ‘predict’ a clinical outcome of interest. Preliminary research has shown that the term prediction was used most often to infer a surrogate marker.
Although revision rate is the benchmark for implant performance, studies using this as an outcome may miss some implant failures. Patients may have declined revision surgery, may have been unfit to undergo revision surgery, or indeed may have been reluctant to seek any medical advice.
Our search only included studies that have been published, thus allowing for potential publication bias that favours statistically significant results. Due to the varied nature and reporting of studies, we have not analysed the methodological quality of each study, nor have we combined the results. Imaging techniques are also limited to detecting movement or wear which is the predominant method of failure in most devices. They may not be able to detect unusual modes of failure such as those observed in MoM devices, where soft-tissue reactions caused local damage before implant loosening occurs. Imaging techniques are also limited by their accuracy in that they cannot measure wear in harder bearings such as metal and ceramic.
Clinical relevance
The recent catastrophic failure of some MoM implants has ignited the debate around current regulation.1,21,51,52 There have been calls for change allowing for the phased introduction of new implants, including the use of RSA in RCTs.5 However, although RSA is useful in most implant types, it can only predict outcome where the mechanism of failure is either migration or wear.19 Therefore, pre-market investigations using RSA must be undertaken in conjunction with detailed post-market surveillance.8,19 In the case of the ASR implant, RSA would not have detected its failure early as it does not detect modes of failure such as trunnion corrosion, elevated metal ions, frictional torque, or edge loading.45 Due to the limits of RSA and EBRA in detecting all modes of failure, other surrogate markers are sought in the post-market surveillance of new implants.
The NJR is an excellent source of information, with almost universal coverage of all THA procedures performed in the United Kingdom, and is therefore highly representative of all types of patients and health professionals.53 However, in its current format it does not recognise problems with implants until they are revised.
Our study revealed numerous studies identifying multiple patient-, surgical- and implant-related factors that are associated with revision rate, but are not surrogate markers. Any post-market surveillance method must adjust for these potential confounding factors.
NJR data (as with other observational studies) are limited by confounding factors, for example, patients and physicians might choose a specific type of prosthesis or surgical approach based on patients’ characteristics or surgeon’s expertise. A recent study investigating the effect of cement on mortality in primary THAs concluded that the NJR does not contain enough details of potential confounders such as pharmaceutical use, comorbidities, socioeconomic status, lifestyle factors (smoking and drinking alcohol) with known impact on longevity.54
The past two decades have seen a significant increase in the number of available implants. In 1995, 62 implants were available for use in primary THA, with demonstrable evidence in 30%.55 In 2011, there was an over four-fold increase to 261, with 24% showing no evidence of clinical effectiveness.5,56 Further calls for change have been made to ensure the identification of failing implants newly introduced on the market. A recent study concluded that the Orthopaedic Data Evaluation Panel benchmark should be reduced from a 10% to a 5% rate of revision at ten years.57 However, there are still issues up to the five-year mark, with some failing devices getting a good rating after three years.1 Therefore, surrogate markers of long-term outcome are urgently needed to ascertain the safety of a new implant within two years of surgery in order to reduce further risk and complication to patients.
Our study has implications to commissioning and regulation of orthopaedic devices. We have shown that the most accurate and reliable validated surrogate marker of outcome for both acetabular and femoral components is RSA. Despite this, RSA can only detect one mode of failure; aseptic loosening; and is inadequate to detect other modes, notably in the case of MoM implants.45 We recommend its use to evaluate all new implants prior to their general release as part of a phased introduction. This is supported by NICE, the IDEAL group and other groups.6,12,13 This should be performed on any implant including new materials and bearing surfaces, irrespective of the argument that they are similar to an existing design.
In conclusion this systematic review has found only two validated surrogate markers which can predict the outcome of long-term primary THA: RSA for measurement of implant migration and wear and EBRA for measurement of wear. We recommend the use of these imaging markers in pre-market testing of new implants as part of a phased introduction. However, there is a need to combine this with post-market surveillance in the phased introduction of new implants. The potential use of the OHS is highlighted for early post-market surveillance, and any post-market surveillance model will need to adjust for a number of patient-, surgical- and implant-related risk factors.
Funding Statement
S. Glyn-Jones reports funding received from Biomet and Zimmer which is not related to this article.
D. Prieto-Alhambra reports funding received from Bioiberica, Amgen and Servier, none of which is related to this article.
We acknowledge the work of Mrs S. Ryan, Liberian, Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre.
ICMJE conflict of interest
None declared.
References
1 Cohen D . Out of joint: the story of the ASR. BMJ2011;342:d2905.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
2 No authors listed. European Commission Enterprise and Industry. http://ec.europa.eu/growth/index_en.htm (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
3 No authors listed. European Commission. Exploring innovative healthcare – the role of medical technology innovation and regulation. http://ec.europa.eu/consumers/sectors/medical-devices/files/exploratory_process/hlc_en.pdf (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]]CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
4 Kynaston-Pearson F , AshmoreAM, MalakTT, et al.. Primary hip replacement prostheses and their evidence base: systematic review of literature. BMJ2013;347:f6956.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
5 McCulloch P , AltmanDG, CampbellWB, et al.. No surgical innovation without evaluation: the IDEAL recommendations. Lancet2009;374-9695:1105-12.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
6 McCulloch P , CookJA, AltmanDG, et al.. IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 1: the idea and development stages. BMJ2013;346:f3012.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
7 Dias J . ‘Beyond Compliance’ – for the safer introduction of Orthopaedic Implants. http://www.beyondcompliance.org.uk/Home.aspx (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
8 No authors listed. National Joint Registry. http://www.njrcentre.org.uk/njrcentre/default.aspx (date last accessed 05 May 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
9 No authors listed. Orthopaedic Evaluation Panel. http://www.odep.org.uk/ (date last accessed 05 May 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
10 Nelissen RG , PijlsBG, KärrholmJ, et al.. RSA and registries: the quest for phased introduction of new implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am2011;93(suppl 3):62-65.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
11 No authors listed. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Total hip replacement and resurfacing arthroplasty for end-stage arthritis of the hip (review of technology appraisal guidance 2 and 44). http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta304/documents/arthritis-of-the-hip-end-stage-hip-replacement-total-and-resurfacing-arthroplasty-rev-ta2-ta44-final-appraisal-determination-document2 (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
12 No authors listed. Metal-on-metal hip replacement Q&A.: Arthritis Research UK. http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/health-professionals-and-students/reports/topical-reviews/topical-reviews-spring-2014.aspx (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
13 de Steiger RN , HangJR, MillerLN, GravesSE, DavidsonDC. Five-year results of the ASR XL Acetabular System and the ASR Hip Resurfacing System: an analysis from the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]2011;93-A:2287-2293.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
14 Ergina PL , BarkunJS, McCullochP, et al.. IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 2: observational studies in the exploration and assessment stages. BMJ2013;346:f3011.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
15 Cook JA , McCullochP, BlazebyJM, et al.. IDEAL framework for surgical innovation 3: randomised controlled trials in the assessment stage and evaluations in the long term study stage. BMJ2013;346:f2820.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
16 Furlan AD , PennickV, BombardierC, van TulderM. 2009 updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976)2009;34:1929-1941.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
17 Ghogomu EA , MaxwellLJ, BuchbinderR, et al.. Updated method guidelines for cochrane musculoskeletal group systematic reviews and metaanalyses. J Rheumatol2014;41:194-205.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
18 McKee AE , FarrellAT, PazdurR, WoodcockJ. The role of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration review process: clinical trial endpoints in oncology. Oncologist2010;15(suppl 1):13-18.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
19 Sesselmann S , ForstR, TschunkoF. Radiostereometric analysis of hip implants: a critical review of methodology and future directions. OA Musculoskeletal Medicine2013;4:31. Google Scholar
20 Pijls BG , NieuwenhuijseMJ, FioccoM, et al.. Early proximal migration of cups is associated with late revision in THA: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 26 RSA studies and 49 survivalstudies. Acta Orthop2012;83:583-591.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
21 Hauptfleisch J , Glyn-JonesS, BeardDJ, GillHS, MurrayDW. The premature failure of the Charnley Elite-Plus stem: a confirmation of RSA predictions. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]2006;88-B:179-183.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
22 Nieuwenhuijse MJ , ValstarER, KapteinBL, NelissenRG. The Exeter femoral stem continues to migrate during its first decade after implantation: 10-12 years of follow-up with radiostereometric analysis (RSA). Acta Orthop2012;83:129-34.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
23 Karrholm J , BorssenB, LowenhielmG, SnorrasonF. Does early micromotion of femoral stem prostheses matter? 4-7-year stereoradiographic follow-up of 84 cemented prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1994;76-B:912-917.PubMed Google Scholar
24 Freeman MA , Plante-BordeneuveP. Early migration and late aseptic failure of proximal femoral prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1994;76-B:432-438.PubMed Google Scholar
25 Krismer M , BiedermannR, StöcklB. The prediction of failure of the stem in THR by measurement of early migration using EBRA-FCA. Einzel-Bild-Roentgen-Analyse-femoral component analysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1999;81-B:273-280.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
26 Krismer M , StocklB, FischerM. Early migration predicts late aseptic failure of hip sockets. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1996;78-B:422-426.PubMed Google Scholar
27 Mazoochian F , SchrimpfFM, KircherJ, et al.. Proximal loading of the femur leads to low subsidence rates: first clinical results of the CR-stem. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg2007;127:397-401.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
28 Hendrich C , SauerU, KirschnerS, SchmitzH, MartellJM. High long-term loosening rate of conical screw cups. Acta Orthop2006;77:886-892.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
29 Takenaga RK , CallaghanJJ, BedardNA, LiuSS, GaoY. Which functional assessments predict long-term wear after total hip arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res2013;471:2586-2594.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
30 Kobayashi A , DonnellyWJ, ScottG, FreemanMA. Early radiological observations may predict the long-term survival of femoral hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1997;79-B:583-589.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
31 Ranawat CS , DeshmukhRG, PetersLE, UmlasME. Prediction of the long-term durability of all-polyethylene cemented sockets. Clin Orthop Relat Res1995;317:89-105.PubMed Google Scholar
32 Dowd JE , SychterzCJ, YoungAM, EnghCA. Characterization of long-term femoral-head-penetration rates. Association with and prediction of osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]2000;82-A:1102-1107.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
33 Malik MH , FisherN, GrayJ, WroblewskiBM, KayPR. Prediction of Charnley femoral stem aseptic loosening by early post-operative radiological features. Int Orthop2005;29:268-271.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
34 Scott G , NakagawaS, OrhanZ, FreemanM. The shortcomings of computer-aided measurement of migration for the prediction of failure of three forms of acetabular fixation by survival analysis and migration study to ten years. Hip Int2006;16:243-249.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
35 Khalily C , WhitesideLA. Predictive value of early radiographic findings in cementless total hip arthroplasty femoral components: an 8- to 12-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty1998;13:768-773.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
36 Nieuwenhuijse MJ , ValstarER, KapteinBL, NelissenRG. Good diagnostic performance of early migration as a predictor of late aseptic loosening of acetabular cups: results from ten years of follow-up with Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis (RSA). J Bone Joint Surg [Am]2012;94-A:874-880.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
37 Harris WH . Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]1969;51-A:737-55.PubMed Google Scholar
38 Pilliar RM , LeeJM, ManiatopoulosC. Observations on the effect of movement on bone ingrowth into porous-surfaced implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res1986;208:108-113.PubMed Google Scholar
39 Soballe K , HansenES, Brockstedt-RasmussenH, BungerC. Hydroxyapatite coating converts fibrous tissue to bone around loaded implants. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1993;75-B:270-278.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
40 Valstar ER , GillR, RydL, et al.. Guidelines for standardization of radiostereometry (RSA) of implants. Acta Orthop2005;76:563-572.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
41 Bottner F , SuE, NestorB, et al.. Radiostereometric analysis: the hip. HSS J2005;1:94-99. Google Scholar
42 Thomas GE , SimpsonDJ, MehmoodS, et al.. The seven-year wear of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial using radiostereometric analysis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]2011;93-A:716-722.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
43 Valstar ER , H S GillR. Radiostereometric analysis in orthopaedic surgery: editorial comment. Clin Orthop Relat Res2006;448:2.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
44 Hurschler C , SeehausF, EmmerichJ, KapteinBL, WindhagenH. Comparison of the model-based and marker-based roentgen stereophotogrammetry methods in a typical clinical setting. J Arthroplasty2009;24-4:594-606.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
45 Penny JO , DingM, VarmarkenJE, OvesenO, OvergaardS. Early micromovement of the Articular Surface Replacement (ASR) femoral component: two-year radiostereometry results. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]2012;94-B:1344-1350.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
46 Krismer M , BauerR, TschupikJ, MayrhoferP. EBRA: a method to measure migration of acetabular components. J Biomech1995;28:1225-1236.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
47 Dumbleton JH , ManleyMT, EdidinAA. A literature review of the association between wear rate and osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty2002;17:649-661.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
48 Rothwell AG , HooperGJ, HobbsA, FramptonCM. An analysis of the Oxford hip and knee scores and their relationship to early joint revision in the New Zealand Joint Registry. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]2010;92-B:413-418.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
49 No authors listed. NHS Information Centre: Finalised Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMS) in England April 2010-March 2011. http://www.hscic.gov.uk/catalogue/PUB07049/fina-prom-eng-apr-10-mar-11-pre-post-rep1.pdf (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
50 Hailer NP , GarellickG, KarrholmJ. Uncemented and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop2010;81:34-41.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
51 Havelin LI , EspehaugB, VollsetSE, EngesaeterLB. The effect of the type of cement on early revision of Charnley total hip prostheses. A review of eight thousand five hundred and seventy-nine primary arthroplasties from the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]1995;77-A:1543-1550.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar
52 Muirhead-Allwood SK . Lessons of a hip failure. BMJ1998;316:644.PubMed Google Scholar
53 No authors listed. The National Joint Registry of England and Wales: The National Joint Registry 11th Annual Report. http://www.njrreports.org.uk/Portals/1/PDFdownloads/NJR%2011th%20Annual%20Report%202014.pdf (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
54 Whitehouse SL , BollandBJ, HowellJR, CrawfordRW, TimperleyAJ. Mortality following hip arthroplasty–inappropriate use of National Joint Registry (NJR) data. J Arthroplasty2014;29:1827-1834. Google Scholar
55 Murray DW , CarrAJ, BulstrodeCJ. Which primary total hip replacement?J Bone Joint Surg [Br]1995;77-B:520-527. Google Scholar
56 No authors listed. The National Joint Registry of England and Wales: The National Joint Registry 9th Annual Report. http://www.njrcentre.org.uk/njrcentre/Portals/0/Documents/England/Reports/9th_annual_report/NJR%209th%20Annual%20Report%202012.pdf (date last accessed 29 February 2016).[[bibmisc]] Google Scholar
57 Kandala NB , ConnockM, Pulikottil-JacobR, et al.. Setting benchmark revision rates for total hip replacement: analysis of registry evidence. BMJ2015;350:h756.CrossrefPubMed Google Scholar










